Cybersecurity in Banking: Threats and Challenges
The digital transformation of the banking sector has undeniably brought about immense convenience, accessibility, and efficiency. However, this increasing adoption of technology, including AI, biometrics, and online banking, has also expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. With multiple digital touchpoints now characterizing banking operations, the risk of cyberattacks has become a critical challenge. As a result, cybersecurity in banking becomes essential for safeguarding sensitive financial data and maintaining trust in the digital financial ecosystem.
What is Cybersecurity in the Banking Industry?
Cybersecurity in banking refers to the set of technologies, protocols, and procedures employed to safeguard financial institutions from cyberattacks. These attacks can include malware, phishing, data breaches, and hacking.
The main objective is to safeguard financial processes, customer data, and the overall integrity and reliability of the bank.
Why is Cybersecurity Important in Banking?
The importance of cybersecurity in banking cannot be overstated. Banks handle enormous amounts of sensitive and confidential information, including personal data, financial transactions, and proprietary business information.
A single breach in a bank's cybersecurity can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
What Are the Prevalent Threats to the Banking Sector?
Cybercrime has evolved into the most significant threat facing the financial industry today. As cybercriminals become increasingly sophisticated, banks and financial institutions struggle to keep pace with these attacks. Here are the cybersecurity challenges faced by the banking sector:
Phishing Attacks:
Gone are the days when criminals needed to dig tunnels and hire a mastermind team to access the money in banks. In the digital age, cyber thieves can do much more damage remotely with very little risk.
Phishing attacks, a common tactic in the realm of cybersecurity in banking, aim to use personal information to make unauthorized financial transactions. These phishing attacks are often disguised as emails, phone calls, text messages, or other communication channels. This type of phishing attack mimics legitimate sources to trick victims into revealing sensitive data, which can be used for unauthorized financial transactions, identity theft, or selling on the black market.
a. Trojans and keyloggers:
Banking trojans are malicious software designed to steal your online banking credentials. These cyber criminals disguise themselves as legitimate apps or websites to trick you into revealing sensitive information.
Once installed, they secretly record your keystrokes, including passwords, account numbers, and OTPs. By creating a convincing illusion of security, these trojans manipulate you into handing over your financial data, leaving you vulnerable to identity theft and financial loss. This highlights a critical aspect of cybersecurity in digital banking i.e. the constant threat of malicious actors who are seeking to exploit user trust and compromise financial information.
Ransomware:
Ransomware is malicious software designed to extort money by encrypting and holding a victim's data hostage. For banks, this can lead to a catastrophic scenario.
Cybercriminals target financial institutions specifically because of the sensitive information they hold. Customer data, financial records, and transaction details are all potential targets for encryption.
When this occurs, banks are locked out of their own systems. All banking operations, from processing payments and managing accounts to internal communications, come to a halt.
This not only disrupts customer services but also causes severe financial and reputational damage to the bank itself. The importance of cybersecurity in banking cannot be overstated in preventing such attacks.
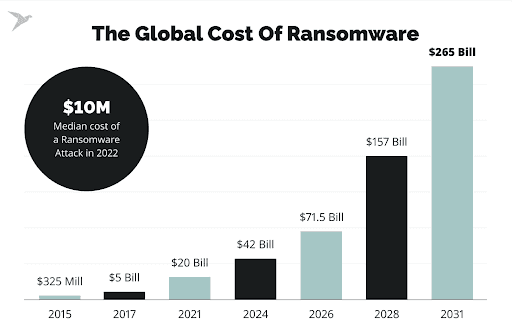
According to Tech Magic's projections, ransomware attacks will inflict $265 billion in damages by 2031.
Read our article on the major ransomware attack targeting the healthcare sector, involving Change Healthcare, and how Health-ISAC responded to this critical breach.
Spoofing:
Clone site attacks are a common cyber threat where hackers create convincing replicas of official bank websites. These fraudulent sites are designed to look and function exactly like the original, often with subtle differences in the URL, such as a misspelled word or altered domain extension.
Hackers distribute links to these clone sites through text messages or emails, tricking users into entering their login credentials. In the context of cybersecurity in banking, implementing multi-factor authentication can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these attacks.
a. Vishing ( Voice Phishing):
Also known as Caller ID spoofing, scammers manipulate the caller ID displayed on your phone to appear as a legitimate business, like your bank. By falsely representing themselves, scammers aim to trick you into sharing sensitive personal information such as account numbers, passwords, CVV numbers, or social security numbers.
b. Email Phishing:
As discussed above, hackers are likely to send out emails with links to these suspicious websites. Here are some phishing email red flags:
- Mismatched Sender Address: Look closely at the sender's email address in the "From" field. The key part is the domain name, which comes after the "@" symbol (e.g., username@domain). Legitimate bank emails will have a domain that matches the bank's official website. Phishing emails often use similar-looking, but fake domains, with slight misspellings or different extensions.
- Requests for Personal Information: Be cautious of emails asking for sensitive information like passwords, account numbers, or social security details. Legitimate banks won't request such information via email.
- Suspicious Links: Don't click on links embedded within the email. Phishing emails may contain links that appear to lead to your bank's website but actually direct you to fraudulent sites designed to steal your information or infect your device with malware (viruses, worms, Trojans, etc.).
Human error is a significant cybersecurity risk. Understanding and mitigating this factor is essential for protecting your organization. Even the most advanced security systems can be compromised by simple mistakes, such as weak passwords or falling for phishing scams.
Supply Chain Attacks:
Supply chain attacks in cybersecurity in banking are different from direct attacks like phishing or malware. Instead of targeting a specific network, they focus on the weaker points in the entire process of banking. This could be anything from the software company itself to the customer's network or even the hardware involved. The goal is still to cause damage, steal money, or access important information, but the route taken to achieve this is indirect and hard to detect.
According to The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency and Lumin Digital, there are 3 types of supply chain attacks:
a. Updates:
Hackers can hide malware in software updates. When companies release updates, attackers can sneak harmful code into them. This lets hackers take control of the computers that install the update.
b. Certificates:
Hackers can bypass security certificates to trick software into installing malicious updates, pretending to be the original developer.
c. Open-source code:
Hackers are hiding malicious code in popular open-source software. This code is widely used by businesses to build their own applications. One sneaky trick is to create fake software that looks almost identical to the real thing, fooling developers into using the harmful version.
The problem is that most companies trust the software they use and focus on protecting their own systems. They don't realize that the danger could come from the software itself.
Examples of Cyberattacks on the Financial Sector in 2024:
Bank of America:
In February, Bank of America was hit by a data breach that involved unauthorized access to customer data, such as credit card information and addresses.
EquilLand:
EquilLand was hit by unauthorized access in January. The company was hit by a ransom attack and the LockBit group took responsibility for the attack. While transaction and customer data were not compromised, the attackers did manage to obtain employee data.
Prudential Financial:
On February 5, Prudential Financial, a Fortune 500 company also detected a data breach. About 36,545 people had been affected. Names, addresses, driving license numbers, and other IDs were taken in the data breach.
Conclusion:
The advantages of high cybersecurity in banking are numerous. Strong cybersecurity solutions can help banks protect their customers' sensitive data, maintain their reputation, and avoid costly financial losses.
Are you a cybersecurity vendor looking to sell your solutions to CISOs in the finance sector?
Execweb can help you sell your solutions by putting you in front of relevant CISOs and other cybersecurity decision-makers. We offer exclusive access to a powerful network: the CISO Executive Network. Imagine a community of Fortune 500 CISOs and top executives – all actively seeking innovative cybersecurity solutions.
Through our platform, you can connect directly with these key decision-makers. This opens doors for selling your services, gathering valuable feedback on your products, and forming strategic partnerships within the industry.
Visit our website and sign up today to unlock the connections that will help your cybersecurity business grow.








Comment